Samsung India Factory Strike: Labor Disputes and Challenges
Background of the Strike
A large-scale strike has been ongoing for a week at Samsung Electronics' Chennai plant in India. This event has had a profound impact on Samsung's operations in India and the overall investment environment in the country. The strike not only exposes the tense labor relations in Indian manufacturing but also presents new challenges to Prime Minister Modi's "Make in India" initiative.
Details of the Incident
 Scale and Demands: The strike involved over 1,000 of the plant's approximately 1,800 workers. The primary reasons for the strike were low wages, poor working conditions, and a lack of union representation. Workers demanded higher wages, improved working hours, and recognition of a union supported by the Centre of Indian Trade Unions (CITU).
Scale and Demands: The strike involved over 1,000 of the plant's approximately 1,800 workers. The primary reasons for the strike were low wages, poor working conditions, and a lack of union representation. Workers demanded higher wages, improved working hours, and recognition of a union supported by the Centre of Indian Trade Unions (CITU).
Police Intervention and Arrests: On September 16th, Chennai police arrested over 100 Samsung employees involved in the strike, citing an "unauthorized" protest march. The union had planned to march to the Kancheepuram district government office but was thwarted by the police, leading to the preventive detention of some union members.
Impact of the Samsung India Factory Strike
1. Impact on Samsung: The strike caused a temporary halt in production at the Chennai plant, significantly affecting Samsung's annual revenue in India. The plant's products account for approximately one-third of Samsung's total revenue in the country. Samsung Electronics has indicated that it will start discussions with workers and unions to resolve all issues as soon as possible.
2. Impact on India: Industry experts believe that this strike casts a shadow over the "Make in India" initiative and may raise concerns among foreign investors about India's investment climate. Investors may reassess their investment strategies in India, considering labor issues and potential social instability.
3. Impact on the Global Supply Chain: The strike has not only attracted domestic attention in India but has also drawn international attention to labor rights and industrial relations in the country. It remains unclear how long the arrested workers will be detained, but the incident has become a focal point of international public opinion.
Comparison and Reflection
It is noteworthy that while the Chennai plant experienced a strike, Samsung's other major plant in Noida has not faced a similar situation. The Noida plant, as Samsung's largest mobile manufacturing facility in India, serves both the domestic market and exports smartphones to other countries. This contrast indicates that labor relations may vary significantly between different plants and reflects the complex challenges faced by India's manufacturing industry during its rapid development.
Conclusion
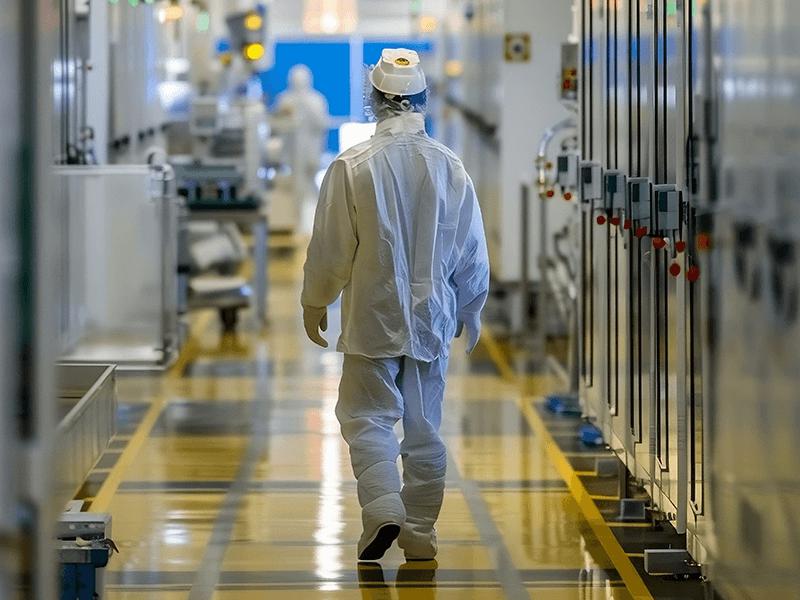 The Samsung India factory strike serves as a reminder that while pursuing rapid industrial development, social justice issues cannot be overlooked. It is imperative to prioritize harmonious and stable labor relations. The government, enterprises, and unions should work together to strengthen communication and cooperation, effectively resolve labor disputes, and create a more favorable environment for sustainable manufacturing development. Only in this way can the "Make in India" initiative move forward smoothly and inject new vitality into India's economic growth.
The Samsung India factory strike serves as a reminder that while pursuing rapid industrial development, social justice issues cannot be overlooked. It is imperative to prioritize harmonious and stable labor relations. The government, enterprises, and unions should work together to strengthen communication and cooperation, effectively resolve labor disputes, and create a more favorable environment for sustainable manufacturing development. Only in this way can the "Make in India" initiative move forward smoothly and inject new vitality into India's economic growth.
About
Samsung
Samsung Group, founded in 1938, is a world-renowned multinational enterprise with businesses covering electronics, finance, machinery, chemistry and other fields. Among them, Samsung Electronics, as the flagship company of the group, is known around the world for its innovative electronic products such as smartphones, TVS, semiconductors, etc. Samsung continues to promote technological innovation and is committed to providing high-quality products and services to meet the needs of consumers around the world.
Hot IC Chip in Conevo Fast Shop
● The BCM569 series is a Broadcom high-performance Ethernet switch chip designed for data center and high-performance networking applications. These chips support high-density port configurations, enabling flexible networking solutions to meet the growing demand for data transmission. The BCM569 series chips use high-speed SerDes technology to support 25GbE, 50GbE, and 100GbE rates, provide a total switching capacity of up to several terabytes /s, support configurations from tens to hundreds of ports, integrate advanced traffic management functions, and support a wide range of virtualization protocols and network functions.
● The MAX31790ATI+T is a motor driver/controller manufactured by Maxim Integrated that controls the speed of up to six fans through six independent PWM (pulse width modulation) outputs. The controller chip also provides a tachometer input function to monitor the fan speed.
● The TPS568215RNNR is a power management chip manufactured by Texas Instruments (TI) for power conversion and voltage regulation. It is a single-chip 8A synchronous buck converter with adaptive on-time D-CAP3 control mode. The TPS568215RNNR is capable of efficiently converting higher input voltages (4.5V to 17V) to lower output voltages (0.6V to 5.5V) and integrates lower power MOSFETs with R DS(on) through precise voltage regulation. The converter chip is widely used in server and storage, set-top boxes, high-end DTV, telecom and networking, point of load (POL), IPC, factory automation and many other fields.
Website: www.conevoelec.com
Email: info@conevoelec.com