Trench-Type SiC MOSFET: An Inevitable Trend in Power Device Development
In the first half of 2024, ON Semiconductor made significant moves in the semiconductor market by launching its second-generation 1200V SiC MOSFET products. These products utilized the M3S process platform (with an M3T branch specifically targeting inverter applications) based on a planar structure, yet achieved notable technological advancements. However, ON Semiconductor recently announced on its official microblog that the next generation M4S and M4T products will adopt trench designs and combine thin wafer technology to reduce the die size by 25%. The M4 process platform will achieve 100% trench utilization, aiming to provide performance unique to traditional planar devices.
01 Structure and Advantages of SiC MOSFET
The development of SiC MOSFET structures has a clear trajectory. Early planar structures were the most common in SiC MOSFET design due to their simplicity and mature, stable processes, leading to large-scale applications. In MOSFETs, cells are the basic repeating units that construct them, with numerous cells connected in parallel to achieve higher current carrying capacity and better thermal distribution.
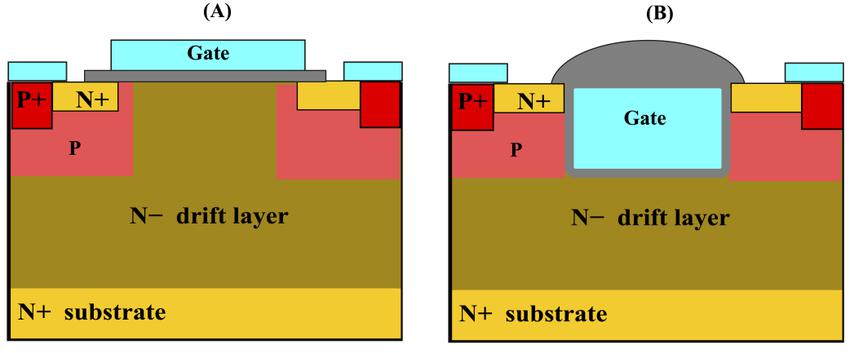
Planar MOSFETs have their advantages. The gate and source electrodes are on the same horizontal plane, with cells independently arranged in an array. The process is simple, allowing for high-quality gate oxide layers, strong voltage surge resistance, and higher reliability under overload conditions. In silicon substrate planar MOSFETs, the combination of oxide and silicon has been extensively studied and designed. Although there is some similarity in SiC, the carbon plays a special role during SiC oxidation, leading to physical serrated areas at the interface that can cause electrical issues. This requires many suppliers to invest time, field experience, and engineering validation to address these issues.
However, from a performance perspective, the conduction capability of MOSFETs depends on the cell spacing. Smaller spacing and higher density can reduce conduction resistance and switching losses, enhance voltage withstand capability, and reduce device size to increase power density. Planar devices are limited by the horizontal layout of the gate, restricting the reduction of cell spacing. Trench-type structures etch cells into the SiC wafer through deep trenches, positioning the gate on the trench sidewalls. This reduces cell spacing, enabling higher current density, lower conduction resistance, and other performance improvements. Additionally, more cells can be accommodated in the same wafer area, reducing chip size under the same specifications.
02 Market Status of Trench-Type SiC MOSFET
In the market, only Infineon and ROHM have mass-produced and widely applied trench-type SiC MOSFETs. Infineon's products have been supplied to XPeng, and ROHM supplies Geely and others. Tesla first launched a model equipped with SiC MOSFETs in 2018, using STMicroelectronics' 650V SiC MOSFETs, which propelled STMicroelectronics to a significant share in the automotive SiC market. STMicroelectronics originally planned to launch trench-type SiC MOSFET products in 2022 but has postponed it to 2025 in this year's roadmap. This is partly because planar types, after large-scale application in automobiles, have gradually improved in process, with performance now meeting automotive application needs and reliability and process consistency reaching a certain level. On the other hand, market demand is not as urgent, and planar types still have room for improvement.
03 Domestic and International Manufacturers' Layout
Several overseas power semiconductor manufacturers are actively laying out trench-type SiC MOSFETs, such as Wolfspeed, Mitsubishi, Fuji, Denso, and UnitedSiC, which was acquired by ON Semiconductor. They have applied for numerous patents, and some have already launched samples. In terms of domestic power SiC manufacturers, most of the mass-produced products are planar types, but they are also actively carrying out trench-type layouts. For example, San'an is expected to launch trench-type SiC MOSFET products in the first quarter of 2025. The latest product introduction from CRRC shows that its SiC MOSFET uses the fourth-generation trench gate technology. Many manufacturers, including Yangjie Technology, Huayi Microelectronics, and SIP Semiconductor, have also laid out patents for trench-type SiC MOSFETs.
04 Conclusion
 In summary, as electric vehicles develop towards high power and low energy consumption, the development of trench-type SiC MOSFETs is an inevitable direction. However, considering that safety is the primary consideration in automotive applications, the importance of reliability is self-evident. Therefore, the transition of SiC MOSFETs from planar to trench types, especially in automotive applications, requires a relatively long process. In this process, domestic and international manufacturers need to continue to invest in R&D resources, strengthen technological innovation, and patent applications to cope with the fierce competition in the future market.
In summary, as electric vehicles develop towards high power and low energy consumption, the development of trench-type SiC MOSFETs is an inevitable direction. However, considering that safety is the primary consideration in automotive applications, the importance of reliability is self-evident. Therefore, the transition of SiC MOSFETs from planar to trench types, especially in automotive applications, requires a relatively long process. In this process, domestic and international manufacturers need to continue to invest in R&D resources, strengthen technological innovation, and patent applications to cope with the fierce competition in the future market.
Conevo Circuit Controll Ics
Looking for the latest and most popular IC parts? Check out Conevo Electronics, your trusted IC distributor, offering quick access to a vast array of IC resources. In the meantime, here is our selection of featured IC components.
● The ME432AXG is a low-voltage, programmable precision voltage regulator designed by Microne, featuring an adjustable output voltage from 1.25V to 18V with high precision of ±0.5% and low temperature coefficient of 30ppm/℃, suitable for applications such as switch-mode power supplies, charging management, and operational amplifier circuits.
● The MMSD4148T1G is a high-speed switching diode from ON Semiconductor, featuring a SOD-123 surface mount package, a high breakdown voltage of 100V, a fast switching time, qualified for automotive and other applications requiring unique site and control change requirements.
● The TM4C123GH6PGEI7 is a 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4F-based microcontroller from Texas Instruments, featuring an 80 MHz operating frequency, 256 KB of Flash memory, 32 KB of SRAM, and a range of communication interfaces including UART, SPI, I2C, and USB 2.0, designed for industrial applications such as remote monitoring and factory automation.
Website: www.conevoelec.com
Email: info@conevoelec.com