Explore the Most Common IC Types for Electrical/Circuit Design
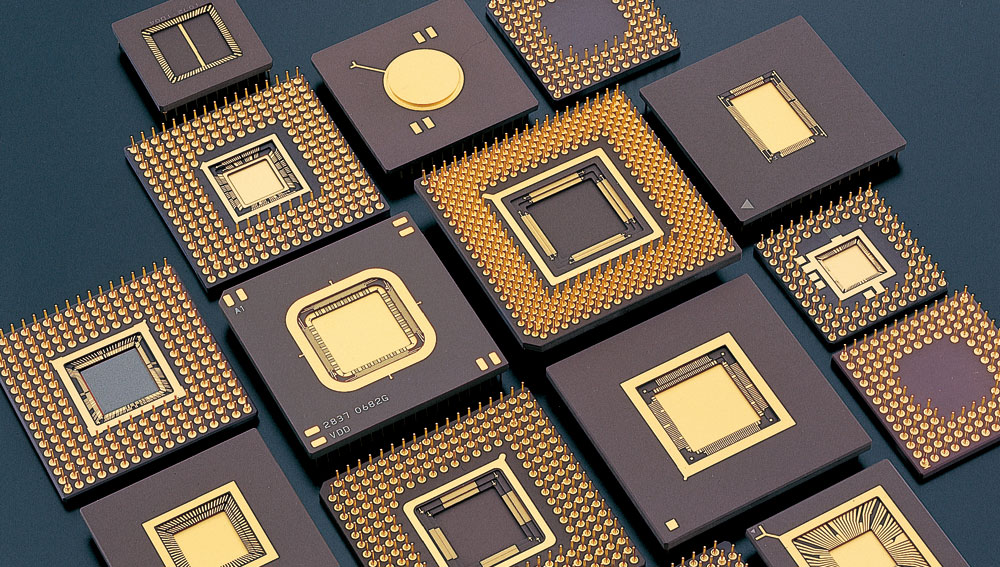
Integrated Circuits (ICs), as the cornerstone of modern electronic technology, have achieved a high degree of integration and miniaturization of electronic components by integrating transistors, resistors, capacitors, and other electronic components onto a tiny semiconductor ic material. Since their inception in the 1960s, IC technology has been widely applied in electrical and circuit design, greatly driving technological innovation and industry development in electronic products. This article will introduce several of the most common IC types and their primary applications in electrical/circuit design.
I. Digital Integrated Circuits (Digital ICs)
Digital ICs are primarily used to process discrete binary signals, represented as 0s and 1s, and excel in logical operations and data processing. In digital electronic products such as computers, smartphones, and digital watches, digital ICs undertake the core data processing tasks. Common digital ICs include microprocessors (such as CPUs and GPUs), memories (such as SRAM, DRAM, ROM, and Flash), and System-on-Chips (SoCs).
● Microprocessors: As the core of computers and other intelligent devices, microprocessors are responsible for executing instructions, processing data, and controlling system operations. For example, the CPU is the "brain" of a computer system, responsible for executing instructions in programs and completing various computational and control tasks.
● Memories: Used to store data and programs for quick access when needed. SRAM and DRAM are common memory types used for cache and main memory, respectively. Flash memory is widely used in Solid State Drives (SSDs) and embedded systems for persistent data storage.
● System-on-Chips (SoCs): Integrate multiple functions such as processors, memories, input/output interfaces, etc., onto a single chip to form a complete system. SoCs are widely used in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, achieving high performance, low power consumption, and low cost.
II. Analog Integrated Circuits (Analog ICs)
Analog ICs process continuously varying analog signals and are indispensable in practical applications such as audio processing, radio signal transmission, and voltage regulation. Common analog ICs include operational amplifiers, linear regulators, and voltage references.
● Operational Amplifiers: Characterized by high gain, high input impedance, and low output impedance, they are widely used in analog signal processing circuits such as audio amplification, signal filtering, and comparison.
● Linear Regulators: Used to provide a stable output voltage and protect circuits from voltage fluctuations. LDOs (Low-Dropout Linear Regulators) are commonly used linear regulators with advantages such as low power consumption, low noise, and high stability.
● Voltage References: Provide a stable reference voltage for voltage comparison and regulation in circuits. The accuracy and stability of voltage references are crucial to circuit performance.
III. Mixed-Signal Integrated Circuits (Mixed-Signal ICs)
Mixed-Signal ICs combine the functionality of digital ICs and analog ICs, capable of processing both analog and digital signals simultaneously. For example, in smartphones, mixed-signal ICs process analog audio signals from microphones, convert them into digital signals for audio encoding and processing, and then convert the processed digital audio signals back into analog signals for playback through speakers. Simultaneously, in wireless communication modules, mixed-signal ICs handle the conversion between radio frequency analog signals and baseband digital signals, enabling wireless data transmission. Common mixed-signal ICs include Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs), Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs), and baseband chips.
● Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs): Convert digital signals to analog signals, widely used in audio and video equipment such as digital audio players and digital TV set-top boxes.
● Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs): Convert analog signals to digital signals for processing and storage by digital circuits. ADCs have widespread applications in sensor interfaces, data acquisition, and signal processing.
● Baseband Chips: Used to process baseband signals in wireless communications, including signal modulation, demodulation, encoding, and decoding. Baseband chips are one of the core components of smartphones, wireless communication base stations, and other devices.
IV. Power Management ICs
Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMICs) are used to control and regulate power in circuits, ensuring stable operation of circuits under various working conditions. Their main functions include voltage regulation, power switch control, battery charging management, etc. For example, in industrial equipment, PMICs can withstand high voltages and large currents, achieving efficient energy conversion and distribution to ensure stable operation of equipment in complex working environments. Common power management ICs include LDOs, DC/DC converters, and PWM controllers.
● LDOs (Low-Dropout Linear Regulators): As mentioned earlier, they are basic power ICs used to provide stable output voltages.
● DC/DC Converters: Convert one DC voltage level to another, offering advantages such as high efficiency, small size, and a wide input voltage range.
● PWM Controllers: Control output voltage or current by adjusting pulse width, achieving voltage regulation or constant current output. PWM controllers have widespread applications in switching power supplies, motor drives, and other
V. Applications of ICs in Electrical/Circuit Design
Different types of ICs play unique roles in electrical/circuit design, collaborating to drive the rapid development of modern electronic technology. Besides the aforementioned common IC types, there are also ICs for specific applications, such as those for televisions, audio systems, and remote controls. These ICs are designed according to specific application requirements and possess unique functions and performances.
In electrical/circuit design, the applications of ICs cover almost all fields. From simple digital logic circuits to complex embedded systems, from power management to signal processing, ICs play an indispensable role. In the design of future electronic devices, a deep understanding and rational use of various IC types will be key to achieving high-performance, low-power, and miniaturized electronic systems. By selecting and using ICs appropriately, the performance of circuits can be significantly improved, costs reduced, and design processes simplified.
Website: www.conevoelec.com
Email: info@conevoelec.com